
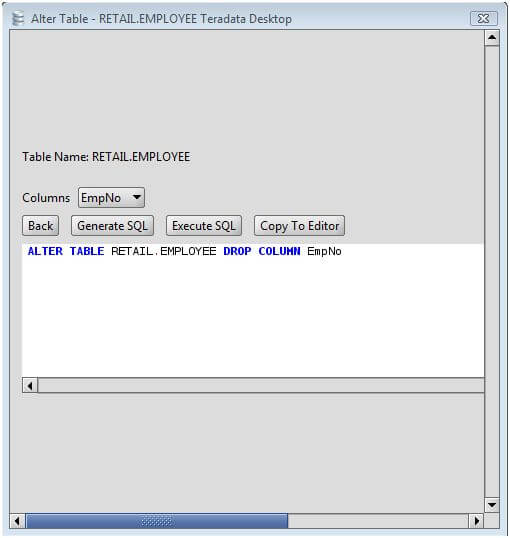
The correct answer depends on the version of the MySQL engine you're using. Mysql> INSERT INTO s_relations_new SELECT * FROM s_relations_old WHERE id > ALTER TABLE s_relations_new RENAME s_relations ĬAVEAT : Once you are satisfied with this operation, you can drop the old table at your earliest convenience: mysql> DROP TABLE s_relations_old Mysql> SELECT MAX(id) INTO FROM s_relations_new Just login to mysql and do the following: mysql> ALTER TABLE s_relations RENAME s_relations_old Now, if you cannot take mysql down, you will have to do a bait-and-switch on s_relations. Then, restart mysql normally $ service mysql restart Mysql> ALTER TABLE s_relations_new RENAME s_relations Mysql> INSERT INTO s_relations_new SELECT * FROM s_relations WHERE id > ALTER TABLE s_relations RENAME s_relations_old Next, login to mysql and load those last rows: mysql> SELECT MAX(id) INTO FROM s_relations_new In the OS, restart mysql so that no one else can log in but (disables TCP/IP): $ service mysql restart -skip-networking To assure that the table is frozen and used only for this update, you must have a little downtime for the sake of getting those last rows that were inserted into s_relation_new. Go find the maximum id in s_relations_new and append everything after that ID from s_relations. If your website has been up this whole time, there may have INSERTs running against s_relations during the loading of s_relations_new. INSERT INTO s_relations_new SELECT * FROM s_relations Once the usefulness or uselessness of those indexes have been determined, you can reload the data #ĪLTER TABLE s_relations_new CHANGE sent_at sent_at_new int(11) DEFAULT NULL If COUNT(DISTINCT target_object_id) > 4,000,000.As a rule of thumb, the MySQL Query Optimizer will not use an index if the cardinality of the selected columns is greater that 5% of the table row count. SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT target_object_id) FROM s_relations Īccording to your question, there are about 80,000,000 rows. SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT message_id) FROM s_relations Run the following queries: SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT sent_at) FROM s_relations Are there any indexes that have low cardinality? Here is the way to determine that: OK That takes care of unnecessary indexes. I dropped target_persona_relation_type_index because the first 2 columns are also in target_persona_relation_type_message_id_index target_persona_relation_type_message_id_index.I dropped target_persona_index because it is the first column in 2 other indexes I dropped source_persona_index because it is the first column in 4 other indexes Here are the initial steps to load a new version of the table CREATE TABLE s_relations_new LIKE s_relations ĭROP INDEX target_persona_relation_type_index

One sure way to speed up an ALTER TABLE is to remove unnecessary indexes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
